Werner’s Nomenclature of Colours
By P. Syme
A recreation of the original 1821 color guidebook with new cross references, photographic examples, and posters designed by Nicholas Rougeux
By P. Syme
A recreation of the original 1821 color guidebook with new cross references, photographic examples, and posters designed by Nicholas Rougeux
Explore all 110 colors painted by Syme with photos of where to find each color as outlined in the original guide.
Decorate your walls with creative data visualizations designed to highlight the beautiful colors used in the original guidebook.
See scans of the original guidebook created by Syme from 1821 that Charles Darwin consulted during his voyages.
These colors are scans of the original swatches Syme painted in the 18th century extracted from the scanned copy on the Internet Archive. While the original colors have aged, they have been preserved here as in the original in an effort to faithfully reproduce the guide. Punctuation and capitalization can be unusual in places because it is the same as in the original.
Snow White, is the characteristic colour of the whites; it is the purest white colour; being free of all intermixture, it resembles new-fallen snow. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Black-headed gull
Photo: Hans Hillewaert
Snowdrop
Photo: Geoff Doggett
Carrara marble
Photo: James St. John
Calcareous sinter
Photo: Michael Linnenbach
Reddish White, is composed of  snow white, with a very minute portion of
snow white, with a very minute portion of  crimson red and
crimson red and  ash grey. W.
ash grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Grey linnet egg
Photo: Didier Descouens
Christmas rose
Porcelain earth
Photo: James St. John
Purplish White, is  snow white, with the slightest tinge of
snow white, with the slightest tinge of  crimson red and
crimson red and  Berlin blue, and a very minute portion of
Berlin blue, and a very minute portion of  ash grey.
ash grey.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Black-legged kittiwake
Photo: Sharp Photography
White geranium
Photo: Tony Hisgett
Storksbill
Photo: David Eickhoff
Aragonite
Photo: Didier Descouens
Yellowish White, is composed of  snow white, with a very little
snow white, with a very little  lemon yellow and
lemon yellow and  ash grey. W.
ash grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Egret
Photo: El Golli Mohamed
Hawthorn blossom
Photo: Mary Hutchison
Chalk
Photo: James St. John
Tripoli
Photo: DYET
Orange-coloured White, is  snow white, with a very small portion of
snow white, with a very small portion of  tile red and
tile red and  king's yellow, and a minute portion of
king's yellow, and a minute portion of  ash grey.
ash grey.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Barn owl
Photo: Alun Williams333
White convulvulus
French porcelain cup
Photo: World Imaging
Greenish White, is  snow white, mixed with a very little
snow white, mixed with a very little  emerald green and
emerald green and  ash grey. W.
ash grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Goldcrest
Photo: Cliff Watkinson
Polyanthus narcissus
Photo: Zachi Evenor
Calcareous sinter
Photo: Michael Linnenbach
Skimmed-milk White, is  snow white, mixed with a little
snow white, mixed with a little  Berlin blue and
Berlin blue and  ash grey. W.
ash grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Eyeball
Photo: Psychonaught
Blue hepatica
Opal
Photo: James St. John
Greyish White, is  snow white, mixed with a little
snow white, mixed with a little  ash grey. W.
ash grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Black-legged kittiwake
Photo: Sharp Photography
White grapes
Photo: Silverije
Limestone
Photo: Hans
Ash Grey, is the characteristic colour of Werner's Greys; he gives no description of its component parts; it is composed of  snow white, with portions of
snow white, with portions of  smoke and
smoke and  French grey, and a very little
French grey, and a very little  yellowish grey and
yellowish grey and  carmine red. W.
carmine red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Long-tailed tit
Photo: Membeth
Wood ashes
Photo: Laurentius
Flint
Photo: Otis Crandell
Smoke Grey, is  ash grey mixed with a little
ash grey mixed with a little  brown. W.
brown. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
European robin
Photo: Michel Langeveld
Flint
Photo: Otis Crandell
French Grey, nearly the steel grey of Werner, without the lustre, is  greyish white, with a slight tinge of
greyish white, with a slight tinge of  black and
black and  carmine red.
carmine red.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Pied Wagtail
Photo: Albert Bridge
Pearl Grey, is  ash grey mixed with a little
ash grey mixed with a little  crimson red and
crimson red and  blue, or
blue, or  bluish grey with a little
bluish grey with a little  red. W.
red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Black-headed gull
Photo: Hobbyfotowiki
Purple Hepatica
Photo: Archenzo Moggio
Porcelain Jasper
Photo: Daderot
Yellowish Grey, is  ash grey mixed with
ash grey mixed with  lemon yellow and a minute portion of
lemon yellow and a minute portion of  brown. W.
brown. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Northern wheatear
Photo: Imran Shah
Barberry bush
Photo: Famartin
Chalcedony
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Bluish Grey, is  ash grey mixed with a little
ash grey mixed with a little  blue. W.
blue. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Wood pigeon
Photo: Tristan Ferne
Limestone
Photo: Hans
Greenish Grey, is  ash grey mixed with a little
ash grey mixed with a little  emerald green, a small portion of
emerald green, a small portion of  black, and a little
black, and a little  lemon yellow. W.
lemon yellow. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
European robin
Photo: Partonez
Ash tree
Photo: Spablab
Greywacke
Photo: Michael C. Rygel
Blackish Grey, a blackish lead grey of Werner without the lustre is  ash grey, with a little
ash grey, with a little  blue and a portion of
blue and a portion of  black.
black.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Nuthatch
Photo: Artur Mikołajewski
Hawthorn
Photo: Karsten Madsen
Flint
Photo: Otis Crandell
Greyish Black, is composed of  velvet black, with a portion of
velvet black, with a portion of  ash grey. W.
ash grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
White-throated dipper
Photo: Ron Knight
Eurasian moorhen
Photo: Luiz Lapa
Basalt
Photo: Jamain
Bluish Black, is  velvet black, mixed with a little
velvet black, mixed with a little  blue and
blue and  blackish grey. W.
blackish grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Black slug
Photo: Prashanthns
Crowberries
Photo: Thomas Quine
Cobalite
Photo: James St. John
Greenish Black, is  velvet black, mixed with a little
velvet black, mixed with a little  brown,
brown,  yellow, and
yellow, and  green. W.
green. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Lapwing
Photo: Andreas Trepte
Hornblende
Photo: James St. John
Pitch, or Brownish Black, is  velvet black, mixed with a little
velvet black, mixed with a little  brown and
brown and  yellow. W.
yellow. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Black guillemot
Photo: Boaworm
Ilvaite (yenite mica)
Photo: Raimond Spekking
Reddish Black, is  velvet black, mixed with a very little
velvet black, mixed with a very little  carmine red, and a small portion of
carmine red, and a small portion of  chestnut brown.
chestnut brown.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Tiger moth
Photo: Kurt Kulac
Pochard duck
Photo: Diliff
Fuchsia berries
Photo: MPF
Olivenite (olive copper ore)
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Ink Black, is  velvet black, with a little
velvet black, with a little  indigo blue in it.
indigo blue in it.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Nightshade berries
Olivenite (olive copper ore)
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Velvet Black, is the characteristic colour of the blacks; it is the colour of black velvet. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Mole
Photo: Stanislaw Szydlo
Black guillemot
Photo: Boaworm
Cowpeas
Photo: David E Mead
Obsidian
Photo: ArnoWinter
Black velvet
Photo: FixiPixi_deluxe
Scotch Blue, is  Berlin blue, mixed with a considerable portion of
Berlin blue, mixed with a considerable portion of  velvet black, a very little
velvet black, a very little  grey, and a slight tinge of
grey, and a slight tinge of  carmine red. W.
carmine red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Blue titmouse
Photo: Francis Franklin
Purple anemone
Photo: Buntysmum
Blue copper ore
Photo: Eric Hunt
Prussian Blue, is  Berlin blue, with a considerable portion of
Berlin blue, with a considerable portion of  velvet black, and a small quantity of
velvet black, and a small quantity of  indigo blue.
indigo blue.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Indigo Blue, is composed of  berlin blue, a little
berlin blue, a little  black, and a small portion of
black, and a small portion of  apple green.
apple green.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Blue copper ore
Photo: Eric Hunt
China Blue, is  azure blue, with a little
azure blue, with a little  prussian blue in it.
prussian blue in it.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Blue beetle (similar to rhynchites nitens)
Photo: Yogendra Joshi
Gentian flower
Photo: Twdragon
Blue copper ore
Photo: Eric Hunt
Azure Blue, is  Berlin blue, mixed with a little
Berlin blue, mixed with a little  carmine red: it is a burning colour. W.
carmine red: it is a burning colour. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Antillean-crested hummingbird
Photo: Charles J. Sharp
Grape hyacinth
Photo: Vera Kratochvil
Gentian flower
Photo: Twdragon
Blue copper ore
Photo: Eric Hunt
Ultramarine Blue, is a mixture of equal parts of  Berlin and
Berlin and  azure blue.
azure blue.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Blue heath butterfly
Photo: Lairich Rig
Borage
Photo: Paasikivi
Lapis lazuli (azure)
Photo: Hannes Grobe
Flax-Flower Blue, is  Berlin blue, with a slight tinge of
Berlin blue, with a slight tinge of  ultramarine blue.
ultramarine blue.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Tortoiseshell butterfly (aka Devil’s Butterfly)
Photo: Charles J Sharp
Flax flower
Photo: Derek Ramsey
Blue copper ore
Photo: Eric Hunt
Berlin Blue, is the pure, or characteristic colour of Werner. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Eurasian jay
Photo: Luc Viatour
Blue hepatica
Sapphire
Photo: Stanislav Doronenko
Verditter Blue, is  Berlin blue, with a small portion of
Berlin blue, with a small portion of  verdigris green.
verdigris green.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Green fluorite
Photo: Ervins Strauhmanis
Greenish Blue, the sky blue of Werner, is composed of  Berlin blue,
Berlin blue,  white, and a little
white, and a little  emerald green. W.
emerald green. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Fennel flower
Photo: 4028mdk09
Turquoise
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Fluorite (aka fluorspar)
Photo: Didier Descouens
Greyish Blue, the smalt blue of Werner, is composed of  Berlin blue, with
Berlin blue, with  white, a small quantity of
white, a small quantity of  grey, and a hardly perceptible portion of
grey, and a hardly perceptible portion of  red. W.
red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Eurasian blue tit
Photo: Luc Viatour
Fennel flower
Photo: 4028mdk09
Iron ore
Photo: Eurico Zimbres
Bluish Lilac Purple, is  bluish purple and
bluish purple and  white.
white.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Lebellula depressa
Photo: Charles J Sharp
Blue lilac
Photo: Alex Borland
Lepidolite
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Bluish Purple, is composed of about equal parts of  Berlin blue and
Berlin blue and  carmine red.
carmine red.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Azure blue butterfly
Photo: D. Gordon E. Robertson
White and purple crocus
Photo: PPD
Violet Purple, violet blue of Werner, is  Berlin blue mixed with
Berlin blue mixed with  red, and a little
red, and a little  brown. W.
brown. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Purple aster
Photo: Hectonichus
Amethyst
Photo: JJ Harrison
Pansy Purple, is  indigo blue, with
indigo blue, with  carmine red, and a slight tinge of
carmine red, and a slight tinge of  raven black.
raven black.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Leaf beetle (chrysomela goettingensis)
Photo: gbohne
Scented violets
Photo: Hans
Bowl made from Derbyshire spar
Photo: Andy Mabbett
Campanula Purple, is  ultramarine blue and
ultramarine blue and  carmine red, about equal parts of each: it is the characteristic colour.
carmine red, about equal parts of each: it is the characteristic colour.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Canterbury bell
Photo: Hectonichus
Campanula persicifolia
Photo: Skalle-Per Hedenhös
Purple fluorite
Photo: Didier Descouens
Imperial Purple, is  azure and
azure and  indigo blue, with
indigo blue, with  carmine red, about equal parts of each.
carmine red, about equal parts of each.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Saffron crocus
Photo: Serpico
Purple fluorite
Photo: Didier Descouens
Auricula Purple, is  plum purple, with
plum purple, with  indigo blue and much
indigo blue and much  carmine red.
carmine red.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Blue Bottle Fly
Photo: Hectonichus
Purple auricula
Photo: Krzysztof Golik
Purple fluorite
Photo: Didier Descouens
Plum Purple, the plum blue of Werner, is composed of  Berlin blue, with much
Berlin blue, with much  carmine red, a very little
carmine red, a very little  brown, and an almost imperceptible portion of
brown, and an almost imperceptible portion of  black. W.
black. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Plum
Purple fluorite
Photo: Didier Descouens
Red Lilac Purple, is  campanula purple, with a considerable portio of
campanula purple, with a considerable portio of  snow white, and a very little
snow white, and a very little  carmine red.
carmine red.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Peacock butterfly
Photo: Charles J Sharp
Red lilac
Photo: Plant Image Library
Purple primrose
Lepidolite
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Lavender Purple, the lavender blue of Werner, is composed of  blue,
blue,  red, and a little
red, and a little  brown and
brown and  grey. W.
grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Peacock butterfly
Photo: Charles J Sharp
Dried lavender
Photo: Ardfern
Purple jasper
Pale Bluish Purple, is  lavender purple mixed with a little
lavender purple mixed with a little  red and
red and  black.†
black.†
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Purple jasper
Celindine Green, is composed of  verdigris green and
verdigris green and  ash grey.‡ W.
ash grey.‡ W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Margaritaria
Photo: Ben Sale
Tussilage leaves
Photo: bdk
Beryl
Photo: James St. John
Mountain Green, is composed of  emerald green, with much
emerald green, with much  blue and a little
blue and a little  yellowish grey. W.
yellowish grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Viridaria
Photo: Alexey Yakovlev
Cudweed
Photo: Hugh Knott
Silver-leaved almond
Beryl
Photo: James St. John
Leek Green, is composed of  emerald green, with a little
emerald green, with a little  brown and
brown and  bluish grey. W.
bluish grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Sea kale
Photo: Nick Saltmarsh
Leeks
Photo: THOR
Prase
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Blackish Green, is  grass green mixed with a considerable portion of
grass green mixed with a considerable portion of  black. W.
black. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Meloe violaceus
Photo: Hectonichus
Cayenne pepper plant
Photo: Mokkie
Serpentinite
Photo: James St. John
Verdigris Green, is composed of  emerald green, much
emerald green, much  Berlin blue, and a little
Berlin blue, and a little  white. W.
white. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Rose-ringed parakeet
Photo: Stephen James McWilliam
Oxidized copper
Photo: Chris Wightman
Bluish Green, is composed of  Berlin blue, and a little
Berlin blue, and a little  lemon yellow and
lemon yellow and  greyish white.
greyish white.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Thrush eggs
Photo: Michiel Thomas
Wild rose
Photo: Antranias
Beryl
Photo: James St. John
Apple Green, is  emerald green mixed with a little
emerald green mixed with a little  greyish white. W.
greyish white. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Broom moth (underside not shown)
Photo: Robert Webster
Chrysoprase
Photo: Jarno
Emerald Green, is the characteristic colour of Werner; he gives no description of the component parts of any of the characteristic colours; it is composed of about equal parts of  Berlin blue and
Berlin blue and  gamboge yellow.
gamboge yellow.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Eurasian Teal
Photo: Phonon.b
Emerald
Photo: Parent Géry
Grass Green, is  emerald green mixed with a little
emerald green mixed with a little  lemon yellow. W.
lemon yellow. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Noble chafer beetle
Photo: Siga
Grass field
Photo: Jsayre64
Pear
Photo: George Hodan
Torbernite (aka uran mica)
Photo: Didier Descouens
Duck Green, W. a new colour of Werner's, added since the publication of his nomenclature; it is composed of  emerald green, with a little
emerald green, with a little  indigo blue, much
indigo blue, much  gamboge yellow, and a very little
gamboge yellow, and a very little  carmine red.
carmine red.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Mallard drake
Photo: Alorin
Yew leaves
Photo: Derek Ramsey
Ceylonite
Photo: Géry PARENT
Sap Green, is  emerald green, with much
emerald green, with much  saffron yellow, and a little
saffron yellow, and a little  chestnut brown.
chestnut brown.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Orange tip butterfly
Photo: hamon jp
Nightshade leaves
Photo: Forest & Kim Starr
Pistachio Green, is  emerald green mixed with a little
emerald green mixed with a little  lemon yellow, and a small quantity of
lemon yellow, and a small quantity of  brown. W.
brown. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Eider drake
Photo: David Merrett
Pear
Photo: George Hodan
Saxifrage
Photo: Christoph Braun
Olivine (aka crysolite)
Photo: Wilson44691
Asparagus Green, is  pistachio green, mixed with much
pistachio green, mixed with much  greyish white. W.
greyish white. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Brimstone butterfly
Photo: Charles J Sharp
Variegated horseshoe geranium
Beryl
Photo: James St. John
Olive Green, is  grass green mixed with much
grass green mixed with much  brown. W.
brown. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Lignum vitae
Photo: TreeWorld Wholesale
Epidote
Photo: Didier Descouens
Oil Green, is  emerald green mixed with
emerald green mixed with  lemon yellow,
lemon yellow,  chestnut brown, and
chestnut brown, and  yellowish grey. W.
yellowish grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Freshwater snail
Nonpareil apple
Photo: Abrahami
Beryl
Photo: James St. John
Siskin Green, is  emerald green mixed with much
emerald green mixed with much  lemon yellow, and a little
lemon yellow, and a little  yellowish white. W.
yellowish white. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Euopean siskin
Photo: Simon Eugster
Colmar pear (drawing)
Photo: Ulysses Prentiss Hedrick
Manks codlin (aka irish pitcher) apple
Torbernite (aka uran mica)
Photo: Didier Descouens
Sulphur Yellow, is  lemon yellow mixed with
lemon yellow mixed with  emerald green and
emerald green and  white. W.
white. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Dragonfly
Photo: André Karwath
Snapdragon
Photo: Sharon Mollerus
Sulphur
Photo: Ben Mills
Primrose Yellow, is  gamboge yellow mixed with a little
gamboge yellow mixed with a little  sulphur yellow, and much
sulphur yellow, and much  snow white.
snow white.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Wax Yellow, is composed of  lemon yellow,
lemon yellow,  reddish brown, and a little
reddish brown, and a little  ash grey. W.
ash grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Water beetle larva
Photo: Donald Hines
Semi opal
Photo: James St. John
Nonpareil apple
Photo: Abrahami
Lemon Yellow, the characteristic colour of the yellow series of Werner, the colour of ripe lemons; W. it is found to be a mixture of  gamboge yellow and a little
gamboge yellow and a little  ash grey: being a mixed colour, it cannot be adopted as the characteristic colour; the characteristic colours of the blues, reds, and yellows ought to be pure and free from all intermixture with any other colour; gamboge, as the purest yellow colour, is adopted instead of lemon yellow, as the characteristic colour of the yellows.
ash grey: being a mixed colour, it cannot be adopted as the characteristic colour; the characteristic colours of the blues, reds, and yellows ought to be pure and free from all intermixture with any other colour; gamboge, as the purest yellow colour, is adopted instead of lemon yellow, as the characteristic colour of the yellows.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Hornet
Photo: PiccoloNamek
Goldilocks
Photo: Magnus Manske
Yellow orpiment
Photo: James St. John
Lemon
Photo: Abhijit Tembhekar
Gamboge Yellow, is the characteristic colour.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
European goldfinch
Photo: Francis C. Franklin
Canary
Photo: RoyBuri
Yellow jasmine
Photo: KENPEI
Sulphur
Photo: Ben Mills
Kings Yellow, is  gamboge yellow, with a small portion of
gamboge yellow, with a small portion of  saffron yellow.
saffron yellow.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Golden pheasant
Photo: H. Zell
Yellow tulip
Photo: Anita Mazur
Cinquefoil
Photo: Olivier Pichard
Saffron Yellow, is  gamboge yellow, with
gamboge yellow, with  gallstone yellow, about equal parts of each.
gallstone yellow, about equal parts of each.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Gallstone Yellow, is  gamboge yellow, with a small quantity of
gamboge yellow, with a small quantity of  Dutch orange, and a minute portion of
Dutch orange, and a minute portion of  honey yellow.
honey yellow.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Gallstones
Photo: George Chernilevsky
Marigold apples
Honey Yellow, is  sulphur yellow mixed with
sulphur yellow mixed with  chestnut brown. W.
chestnut brown. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Bird-of-paradise
Photo: joelfotos
Yellow fluorite (aka fluorspar)
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Straw Yellow, is  sulphur yellow mixed with much
sulphur yellow mixed with much  greyish white and a little
greyish white and a little  ochre yellow. W.
ochre yellow. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Polar bear
Photo: Arturo de Frias Marques
Straw
Photo: Caerbannog
Tourmaline (aka schorlite)
Photo: Rob Lavinski
Hemimorphite (aka calamine)
Photo: Rob Lavinski
Wine Yellow, is  sulphur yellow mixed with
sulphur yellow mixed with  reddish brown and
reddish brown and  grey, with much
grey, with much  snow white. W.
snow white. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Silk moth
Photo: CSIRO
White currants
Photo: Mako
Yellow topaz
Photo: James St. John
Sienna Yellow, is  primrose yellow, with a little
primrose yellow, with a little  ochre yellow.
ochre yellow.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Bird-of-paradise feathers
Photo: Daderot
Honeysuckle
Photo: Aftabbanoori
Yellow topaz
Photo: James St. John
Ochre Yellow, is  sienna yellow, with a litlte light
sienna yellow, with a litlte light  chestnut brown. W.
chestnut brown. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Redstart
Photo: Dan Pancamo
Yellow jasper
Photo: Nzfauna
Cream Yellow, is  ochre yellow mixed with a little
ochre yellow mixed with a little  white and a very small quantity of
white and a very small quantity of  Dutch orange. W.
Dutch orange. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Dutch Orange, the orange yellow of Werner, is  gamboge yellow, with
gamboge yellow, with  carmine red. W.
carmine red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Goldcrest
Photo: Cliff Watkinson
Marigold
Photo: Ezhuttukari
Spindle tree seed pods
Orpiment streak
Photo: Ra'ike
Buff Orange, is  sienna yellow, with a little
sienna yellow, with a little  Dutch Orange.
Dutch Orange.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Orpiment Orange, the characteristic colour, is about equal parts of  gamboge yellow and
gamboge yellow and  arterial blood red.
arterial blood red.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Warty newt
Photo: Connor Long
Golden pheasant
Photo: H. Zell
Indian cress
Photo: George Chernilevsky
Brownish Orange, is  orpiment orange, with a little
orpiment orange, with a little  hyacinth red, and a small quantity of light
hyacinth red, and a small quantity of light  chestnut brown.
chestnut brown.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Flesh fly
Photo: Muhammad Mahdi Karim
Orange lily
Photo: Uoaei1
Orange topaz
Photo: Thomas Quine
Reddish Orange, is  buff orange mixed with a considerable portion of
buff orange mixed with a considerable portion of  tile red.
tile red.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Tiger moth
Photo: Kurt Kulac
Hemimeris
Photo: virginie-l
Hibiscus
Photo: Livioandronico2013
Deep Reddish Orange, is  Dutch orange mixed with much
Dutch orange mixed with much  scarlet red.
scarlet red.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Tile Red, is  hyacinth red mixed with much
hyacinth red mixed with much  greyish white, and a small portion of
greyish white, and a small portion of  scarlet red. W.
scarlet red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Bullfinch
Photo: spacebirdy
Pimpernel
Photo: Alvesgaspar
Red jasper
Photo: James St. John
Hyacinth Red, is  scarlet red, with
scarlet red, with  lemon yellow and a minute proportion of
lemon yellow and a minute proportion of  brown.
brown.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Fruit fly (lygœns apterus)
Photo: Sanjay Acharya
Goldrenette apple
Photo: Frank C. Müller
Zircon (aka hyacinth)
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Scarlet Red, is  arterial blood red, with a little
arterial blood red, with a little  gamboge yellow.
gamboge yellow.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Scarlet ibis
Photo: J. Patrick Fischer
Red grouse
Photo: MPF
Oriental poppy
Photo: RoyBoy
Cowpeas
Photo: David E Mead
Cinnabar (aka cinnaber)
Photo: JJ Harrison
Vermilion Red, is  scarlet red, with a minute portion of
scarlet red, with a minute portion of  brownish red. W.
brownish red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Red coral
Photo: Arturo Donate
Wax apple (aka love apple)
Photo: M0rphzone
Cinnabar (aka cinnaber)
Photo: JJ Harrison
Aurora Red, is  tile red, with a little
tile red, with a little  arterial blood red, and a slight tinge of
arterial blood red, and a slight tinge of  carmine red. W.
carmine red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Pied woodpecker
Photo: soumyajit nandy
Apple
Photo: Paolo Neo
Red orpiment
Photo: Parent Gééry
Aterial Blood Red, is the characteristic colour of the red series.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
European goldfinch
Photo: Francis C. Franklin
Corn poppy
Photo: Zeynel Cebeci
Flesh Red, is  rose red mixed with
rose red mixed with  tile red and a little
tile red and a little  white. W.
white. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Light skin
Photo: Helena Paffen
Larkspur
Photo: Heron
Baryte (aka heavy spar)
Photo: Dlloyd
Pink limestone
Photo: James St. John
Rose Red, is  carmine red, with a great quantity of
carmine red, with a great quantity of  snow white, and a very small portion of
snow white, and a very small portion of  cochineal red. W.
cochineal red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Rose
Photo: Vera Kratochvil
Pyrophyllite (a variety of agalmatolite aka figure stone)
Photo: Toma1974
Peach Blossom Red, is  lake red mixed with much
lake red mixed with much  white. W.
white. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Peach blossom
Photo: Dennis Brown
Erythrite (aka red copper ore)
Photo: Géry Parent
Carmine Red, the characteristic colour of Werner is  lake red, with a little
lake red, with a little  arterial blood red. W.
arterial blood red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Raspberries
Photo: Fir0002
Cockscomb
Photo: Lander
Carnation
Photo: Gordon Bell
Ruby
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Lake Red, the crimson red of Werner, is  arterial blood red, with a portion of
arterial blood red, with a portion of  Berlin blue. W.
Berlin blue. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Tulip
Photo: ArielGold
Rose officinalus (aka French or apothecary’s rose)
Photo: Col Ford and Natasha de Vere
Spinel gems
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Crimson Red, is  carmine red, with a little
carmine red, with a little  indigo blue. W.
indigo blue. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Garnet
Photo: James St. John
Purplish Red, the columbine red of Werner, is  carmine red, with a little
carmine red, with a little  Berlin blue, and a small portion of
Berlin blue, and a small portion of  indigo blue. W.
indigo blue. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Turaco (aka terico)
Photo: DickDaniels
Rose officinalus (aka French or apothecary’s rose)
Photo: Col Ford and Natasha de Vere
Garnet
Photo: James St. John
Cochineal Red, is  lake red mixed with
lake red mixed with  bluish grey. W.
bluish grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Sweet William catchfly (aka none-so-pretty)
Photo: T.Voekler
Cinnabar (aka cinnaber)
Photo: JJ Harrison
Veinous Blood Red, is  carmine red mixed with
carmine red mixed with  brownish black. W.
brownish black. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Venous blood
Photo: Tannim101
Musk thistle
Photo: DM
Pincusion flower (scabiosa)
Photo: Mickey JT
Pyrope
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Brownish Purple Red, the cherry red of Werner, is  lake red mixed with
lake red mixed with  brownish black and a small portion of
brownish black and a small portion of  grey. W.
grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Nightshade flower
Photo: GFDLA
Antimony
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Chocoloate Red is  veinous blood red mixed with a little
veinous blood red mixed with a little  brownish red. W.
brownish red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Brownish Red, is  chocolate red mixed with
chocolate red mixed with  hyacinth red and a little
hyacinth red and a little  chestnut brown. W.
chestnut brown. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Red-throated loon (aka diver)
Photo: Ómar Runólfsson
Chert (aka iron flint)
Photo: James. St. John
Deep Orange-coloured Brown, is  chestnut brown, with a little
chestnut brown, with a little  reddish brown, and a small quantity of
reddish brown, and a small quantity of  orange brown.
orange brown.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Pochard duck
Photo: Diliff
Aulstralian shelduck (aka sheldrake)
Photo: JJ Harrison
Cattails
Photo: Arto J
Deep Reddish Brown, is  chestnut brown with a little
chestnut brown with a little  chocolate red.
chocolate red.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Pochard duck
Photo: Diliff
Eurasian teal
Photo: Koshy Koshy
Panicum (aka panic grass)
Photo: Marco Schmidt
Brown blende
Photo: Dave Dyet
Umber Brown, is  chestnut brown, with a little
chestnut brown, with a little  blackish brown.
blackish brown.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Marsh harrier
Photo: Sumeet Moghe
Rudbeckia (aka rubeckia)
Photo: Dcoetzee
Chestnut Brown, the characteristic colour of the browns of Werner's series, W. is  deep reddish brown and
deep reddish brown and  yellowish brown.
yellowish brown.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Yellowish Brown, is  chestnut brown mixed with a considerable portion of
chestnut brown mixed with a considerable portion of  lemon yellow. W.
lemon yellow. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Guinea pig
Photo: Jay Reed
Hoopoe
Photo: Jaiprakashsingh
Chert (aka iron flint)
Photo: James. St. John
Brown jasper
Photo: Tommy
Wood Brown, is  yellowish brown mixed with
yellowish brown mixed with  ash grey.
ash grey.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Weasel
Photo: Cecil Sanders
Snipe
Photo: JJ Harrison
Hazelnuts
Photo: Fir0002
Mountain wood
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Liver Brown, is  chestnut brown mixed with a little
chestnut brown mixed with a little  black and
black and  olive green.
olive green.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Hen pheasant
Photo: Andy Vernon
Hawfinch (grosbeak)
Photo: Serge Serebro
Semi opal
Photo: James St. John
Hair Brown, is  clove brown mixed with
clove brown mixed with  ash grey. W.
ash grey. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Pintail duck
Photo: Petar Milošević
Wood tin
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Broccoli Brown, is  clove brown mixed with
clove brown mixed with  ash grey, and a small tinge of
ash grey, and a small tinge of  red. W.
red. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Black-headed gull
Photo: Hans Hillewaert
Zircon (aka hyacinth)
Photo: Rob Lavinsky
Olive Brown, is  ash grey mixed with a little
ash grey mixed with a little  blue,
blue,  red, and
red, and  chestnut brown.§ W.
chestnut brown.§ W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Kestrel (aka kestril)
Photo: Andreas Trepte
Black currants
Photo: Paolo Neo
Axinite
Photo: Parent Gééry
Blackish Brown, is composed of  chestnut brown and
chestnut brown and  black. W.
black. W.
The colors in these photos are approximate and are intended to serve as examples of where to find the colors described in nature. Contribute your photo »
Storm petrel
Photo: Charles J. Sharp
Black guillemot
Photo: Boaworm
Ferret (aka foulmart)
Photo: USFWS Mountain Prairie
Mineral pitch
Photo: Dave Dyet
Decorate your walls with posters designed based on Werner’s Nomenclature of Colours. Starting at $27.80 for 36″ × 24″.
The entire collection of colors developed by Werner and the colors that were combined to create each one. Includes scans each swatch painted by Syme.



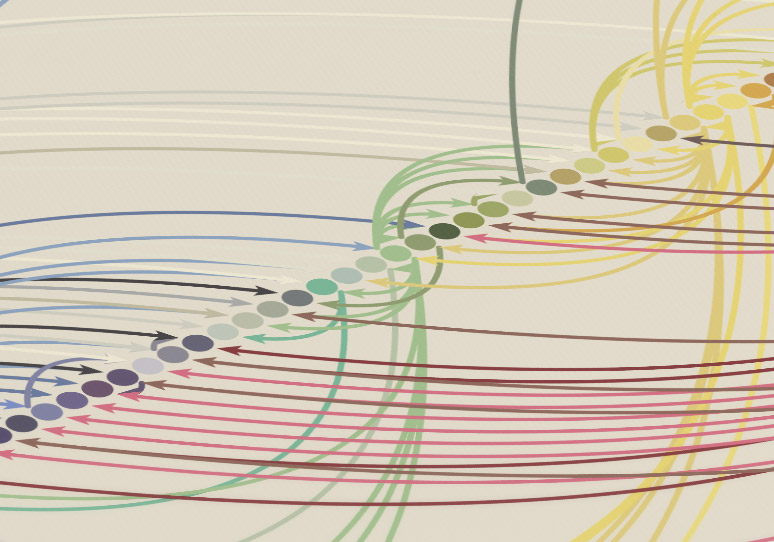
Illustration of which colors were blended into others that Syme painted based on the order listed in the guidebook.


Before photography became commonplace, colorful details were often captured by the written word and Werner’s guidebook served as one of the best guides for classification. Charles Darwin even consulted it for reference during his voyages on the HMS Beagle while researching natural history.
In the late 18th century, German mineralogist Abraham Werner devised a standardized scheme for classifying colors which was later adapted and revised in the 19th century by Scottish painter Patrick Syme.
Syme enhanced Werner’s original guide by including painted swatches for each color based on Werner’s precise descriptions and examples of where to find the colors in the natural world.
The first edition was published in 1814 later in 1821 with minor revisions and some additional observations in the preface for how color classification systems are used in various areas of scientific study.
Below are some scans from the 1821 publication scan available on the Internet Archive.
The 1814 publication was also recently republished by Smithsonian Books.


Below is the complete text of the preface to the original second edition of Werner’s Nomenclature of Colours and the list of colors that were changed from Werner’s original arrangement when Syme adapted it.
A nomenclature of colours, with proper coloured examples of the different tints, as a general standard to refer to in the description of any object, has been long wanted in arts and sciences. It is singular, that a thing so obviously useful, and in the description of objects of natural history and the arts, where colour is an object indispensably necessary, should have been so long overlooked. In describing any object, to specify its colours is always useful; but where colour forms a character, it becomes absolutely necessary. How defective, therefore, must description be when the terms used are ambiguous; and where there is no regular standard to refer to. Description without figure is generally difficult to be comprehended; description and figure are in many instances still defective; but description, figure, and colour combined form the most perfect representation, and are next to seeing the object itself. An object may be described of such a colour by one person, and perhaps mistaken by another for quite a different tint: as we know the names of colours are frequently misapplied; and often one name indiscriminately given to many colours. To remove the present confusion in the names of colours, and establish a standard that may be useful in general science, particularly those branches, viz. Zoology, Botany, Mineralogy, Chemistry, and Morbid Anatomy, is the object of the present attempt.
The author, from his experience and long practice in painting objects which required the most accurate eye to distinguish colours, hopes that he will not be thought altogether unqualified for such an undertaking. He does not pretend indeed that it is his own idea; for, so far as he knows, Werner is entitled to the honour of having suggested it. This great mineralogist, aware of the importance of colours, found it necessary to establish a Nomenclature of his own in his description of minerals, and it is astonishing how correct his eye has been; for the author of the present undertaking went over Werner’s suites of colours, being assisted by Professor Jameson, who was so good as arrange specimens of the suites of minerals mentioned by Werner, as examples of his Nomenclature of Colours. He copied the colours of these minerals, and found the component parts of each tint, as mentioned by Werner, uncommonly correct. Werner’s suites of colours extend to seventy-nine tints. Though these may answer for the description of most minerals, they would be found defective when applied to general science: the number therefore is extended to one hundred and ten, comprehending the most common colours or tints that appear in nature. These may be called standard colours; and if the terms pale, deep, dark, bright, and dull, be applied to any of the standard colours, suppose crimson, or the same colour tinged lightly with other colours, suppose grey, or black, or brown, and applied in this manner:
If all the standard colours are applied in this manner, or reversed, as grey tinged with crimson, &c. the tints may be multiplied to upwards of thirty thousand, and yet vary very little from the standard colours with which they are combined. The suites of colours are accompanied with examples in, or references to, the Animal, Vegetable, and Mineral Kingdoms, as far as the author has been able to fill them up, annexed to each tint, so as to render the whole as complete as possible. Werner, in his suites of colours, has left out the terms Purple and Orange, and given them under those of Blue and Yellow; but, with deference to Werner’s opinion, they certainly are as much entitled to the name of colours as green, grey, brown, or any other composition colour whatever, and in this work Orange and Purple are named, and arranged in distinct places. To accomplish which, it was necessary to change the places of two or three of Werner’s colours, and alter the names of a few more; but, to avoid any mistake, the letter W. is placed opposite to all Werner’s colours. Those colours in Werner’s suites, whose places or names are changed, are also explained, by placing Werner’s term opposite to the name given, which was found more appropriate to the component parts of the changed colours. Those who have paid any attention to colours, must be aware that it is very difficult to give colours for every object that appears in nature; the tints are so various, and the shades so gradual, they would extend to many thousands: it would be impossible to give such a number, in any work on colours, without great expence; but those who study the colours given, will, by following Werner’s plan, improve their general knowledge of colours; and the eye, by practice, will become so correct, that by examining the component parts of the colour of any object, though differing in shade or tint from any of the colours given in this series, they will see that it partakes of, or passes into, some one of them. It is of great importance to be able to judge of the intermediate shades or tints between colours, and find out their component parts, as it enables us correctly to describe the colour of any object whatever.
Werner’s plan for describing the tints, or shades between colours, is as follows: “When one colour approaches slightly to another, it is said to incline towards it; when it stands in the middle between two colours, it is said to be intermediate; when, on the contrary, it evidently approaches very near to one of the colours, it is said to fall, or pass, into it.” In this work the metallic colours are left out, because, were they given, they would soon tarnish; and they are in some measure unnecessary, as every person is well acquainted with the colour of gold, silver, brass, copper, &c. Also the play and changeability of colour is left out, as it is impossible to represent them; however, they are well known to be combinations of colours, varying as the object is changed in position, as in the pigeon’s neck, peacock’s tail, opal, pearl, and other objects of a similar appearance. To gain a thorough knowledge of colours, it is of the utmost consequence to be able to distinguish their component parts. Werner has described the combinations in his suites of colours, which are very correct; these are given, and the same plan followed, in describing those colours which are added in this series. The method of distinguishing colours, their shades, or varieties, is thus described by Werner: “Suppose we have a variety of colour, which we wish to refer to its characteristic colour, and also to the variety under which it should be arranged, we first compare it with the principal colours, to discover to which of them it belongs, which, in this instance, we find to be green. The next step is to discover to which of the varieties of green in the systern it can be referred. If, on comparing it with emerald green, it appears to the eye to be mixed with another colour, we must, on comparison, endeavour to discover what this colour is: if it prove to be greyish white, we immediately refer it to apple green; if, in place of greyish white, it is intermixed with lemon yellow, we must consider it grass green; but if it contains neither greyish white nor lemon yellow, but a considerable portion of black, it forms blackish green. Thus, by mere ocular inspection, any person accustomed to discriminate colours correctly, can ascertain and analyse the different varieties that occur in the Animal, Vegetable, and Mineral Kingdoms. In an undertaking of this kind, the greatest accuracy being absolutely necessary, neither time nor pains have been spared to render it as perfect as possible; and it being also of the first importance, that the colours should neither change nor fade, from long practice and many experiments, the author has ascertained that his method of mixing and laying on colours will ensure their remaining constant, unless they are long exposed to the sun, which affects, in some degree, all material colours; he has therefore arranged Werner’s suites of colours, with his own additions, into a book, and in that form presents it to men of science, trusting, that by removing the present ambiguity in the names of colours, this Nomenclature will be found a most useful acquisition to the arts and sciences.
Since the former edition of this Work was published, Professor Jameson, in his “Treatise on the External Characters of Minerals,” makes the following observations.
“Many attempts have been made to delineate the different colours that occur in the Mineral Kingdom, with the view of enabling those who do not possess a mineralogical collection, or who may not be familiar with colours, to know the different varieties mentioned in the descriptions of mineralogists. Wiedemann, Estner, Ludwig, and several others, have published tables of this kind; but all of them were deficient, not only in accuracy, but also in durability. Having the good fortune to possess a Colour-Suite of Minerals, made under the eye of Werner, by my late friend H. Meuder of Freyberg, and being desirous of making this collection as generally useful as possible, I mentioned my wish to Mr Syme, painter to the Wernerian and Horticultural Societies, who readily undertook to make a delineation of all the varieties in the collection. This he executed with his usual skill and accuracy; adding, at the same time, to the series several other colours, which he has distinguished by appropriate names, and arranged along with those in the Wernerian System. The whole have been published in a series of tables, in a treatise which ought to be in the hands of every mineralogist, and indeed in the possession of naturalists of every description.
“The older and some of the modern mineralogists, in their descriptions of the species of minerals, use only single varieties of colour. It was Werner who first made the remark, that single varieties are not characteristic, and that it is only by using the whole range or suite of the mineral, that we are enabled to employ this character with advantage. Thus, it is not sufficient to say that epidote is green, that beryl is green, or that topaz is yellow; we must mention every variety of colour which these minerals possess, because each species of mineral is expressed by a particular suite or group of colours.
“Although colours are frequently applied by botanists for distinguishing species of plants, particularly in the class cryptogamia, still they in general hesitate in employing them in the discrimination of plants in the higher divisions of the system. It is alleged that the colours of plants change very readily, particularly when cultivated in our gardens, and that, therefore, so variable a character should not be attended to. It is not denied, that the colours of plants frequently undergo very considerable changes when cultivated in our gardens; but these domesticated plants are no longer the natural unaltered species, and therefore are not objects of the attention of the systematic botanist. It is also known, that plants, even in their natural situations, owing to disease, experience great changes in their colours; but these diseased individuals would surely never be taken by the botanist for characteristic examples of the species. Indeed it is highly probable, that every species of plant, in its natural region, has a determined colour, or suite of colours. Hence colours may be used as a most interesting character, particularly in those systems of botany which are termed Natural.
“This character may also be advantageously used in giving correct ideas of the changes of colour which plants experience by cultivation, or when removed from their natural soil and climate. Interesting coloured maps might be constructed, to shew the general changes in the colour of the vegetable world from the equator towards the poles; and the difference of colours in vegetables in the two hemispheres, and in the Old and New World.
“In the Animal Kingdom, the number of colours is very great. They often form the most striking feature in the external appearance of the species; and hence have been considered by systematics as affording discriminating characters of much value. The agriculturist, engaged in the breeding of animals, often witnesses striking changes in their colours, and these varieties of colour, either alone, or conjoined with other characters, characterize his different breeds. But here, as in botany, a regular systematic Nomenclature of Colour is much wanted.
“The anatomist will find it much to his advantage, to use in his descriptions some regular and fixed standard of colours; and in Morbid Anatomy, in particular, the importance of such an aid will be immediately perceived: Thus, the various changes in the animal system, from the slightest degree of inflammation to complete gangrene, are strikingly marked by the different colours the parts assume. Accurate enumerations of these colours as they occur in single varieties, or in groups, conjoined with descriptions of the changes in form, transparency, lustre, consistency, hardness, structure, and weight, observable in the diseased parts, will convey an accurate conception of the diseased parts to those who have not an opportunity of seeing it. But to effect this, the anatomist and surgeon must agree on some fixed nomenclature, not only of colour, but also of form, transparency, lustre, consistency, hardness, and structure; and a better model cannot be pointed out than that contrived by Werner, for the description and discrimination of minerals.
“Lastly, the chemist will have daily opportunities of experiencing its utility; and the meteorologist, and the hydrographer, by the use of an accurate and standard table of colours, will be enabled, in a much more satisfactory manner than heretofore, to describe the sides and meteors of different countries, and the numerous varieties of colour that occur in the waters of the ocean, of lakes and rivers.”
Changed from Werner’s arrangement.
| Werner’s Names | Changed to |
|---|---|
| Milk White. | Skimmed Milk White. |
| Blackish Lead Grey, but without lustre. | Blackish Grey. |
| Steel Grey, but without lustre. | French Grey. |
| Smalt Blue. | Greyish Blue. |
| Sky Blue. | Greenish Blue. |
| Violet Blue. | Violet Purple. |
| Plum Blue. | Plum Purple. |
| Lavender Blue. | Lavender Purple. |
| Orange Yellow. | Dutch Orange. |
| Crimson Red. | Lake Red. |
| Columbine Red. | Purplish Red. |
| Cherry Red. | Brownish Purple Red. |
This is a project from me, Nicholas Rougeux. I created this project to enhance Werner’s Nomenclature of Colours by adding information that I wanted when I read the guidebook, like easily jumping to any color, seeing the colors referenced in the description, and seeing photos of what Werner referenced for his descriptions of each color.
I recognize the system Werner devised isn’t as useful as it used to be when it was devised so many years ago but I enjoy breathing new life into classic works of art so I chose to recreate it online.
The result is something that’s hopefully interesting for those just discovering Werner’s guide and those that may already be familiar with it and want to discover it in a new light.
See my portfolio for more projects.
Werner’s nomenclature of colours : with additions, arranged so as to render it highly useful to the arts and sciences, particularly zoology, botany, chemistry, mineralogy, and morbid anatomy : annexed to which are examples selected from well-known objects in the animal, vegetable, and mineral kingdoms by Patrick Syme, 1821, available from the Internet Archive. Original book not in copyright.
Very special thanks is owed to Bee Ostrowsky, whose diligence in researching accurate avian photography is greatly appreciated.















































































































































































































































































































